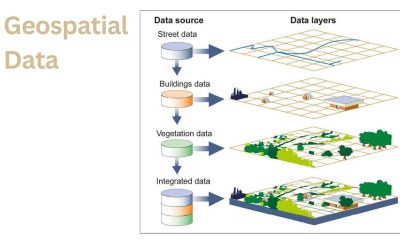
Welcome to my blog, where we explore the fascinating world of geospatial data! Have you ever wondered how analysts use Python to make sense of complex...


Quite like everything else, online dating has changed considerably over the last few years. It has evolved with new and advanced technologies being utilized to fetch...


What is geofencing? The origins of this technology go back as far as the 1960s. Geofencing is in cahoots with Global Positioning System (GPS) first developed...
Recent Comments