Software Development
Real-Time Information Processing in the Age of IoT

By now, everyone ought to know what the Internet-of-Things (IoT) is and what it entails. IoT Analytics noted in 2018 that the number of connected devices in the world crossed seven billion and that the market was accelerating in its adoption []. However, having a connected device and being unable to garner information from that device’s data is counterintuitive. The age of IoT is upon us, and with it comes the need to understand how to tap into streaming data and make the most of it.
How Did We Get Here?
There is a trend in electronics to aim for smaller devices with lower power consumption while keeping the functionality of the item intact. Sensors were a part of commercial business for a long time, but they weren’t connected to each other. The sensor knew its data but was unaware of the world around it. Since 2012, two significant advancements have shifted the focus of sensors away from just knowing its own data and into sharing that data to other devices:
- Communications Improved: Wireless network standards and connectivity rose to prominence. Improvements in communication technology have seen wireless networking change standards. Action Tec notes that today’s wireless routers on the 802.11ac standard are forty times faster than the first wireless routers to hit the market in 1999.
- Sensors Got Better: manufacturing capabilities and technology made it possible to shrink sensors down to a microscopic size while retaining their functionality. The reduced size allowed them to find a home in unique places like shipping containers or clothing without having to worry about if they would get broken or damaged in transit.
The IoT still has a long way to go. However, with the promise of even more stable and secure network communication with the announcement of 5G, there’s a real possibility that more companies will adopt the IoT as a significant part of their data gathering and analytics.
Understanding Big Data in IoT Terms
When looking at the IoT, there’s something that might not immediately be evident. Considering a single IoT device in isolation can be misleading. In reality, a company’s IoT implementation might have hundreds, even thousands of embedded IoT devices, all communicating with each other and the central data store at the same time. The resulting data can be massive, and the industry has coined the term “Big Data” to refer to it. Many companies that have leveraged Big Data as a part of their IoT initiative still find it a hassle to process this data to achieve timely insights. Luckily, there’s another methodology for handling the massive amounts of incoming data from IoT deployments.
Introducing Streaming Data Processing
In May of 2019, Lightbend reported that IoT experienced a threefold increase in real-time processing compared to 2017. Streaming processing uniquely sees data differently from traditional methods. Traditionally, data processing is done on data sets by loading them into memory and doing operations on them to garner results. Streaming data isn’t stored, but as the information is collected and sent to the centralized server, it is processed in real-time, offering faster insights and a quicker rate of consumption of data.
Streaming analytics is how businesses take this incoming data stream and turn it into actionable results. Companies are beginning to realize the benefits of having data streams that can offer them in-depth knowledge about whatever their IoT devices are connected to. The Big Data approach is still valid, and companies that have invested a lot of time and effort into their Big Data infrastructure don’t need to replace it. Streaming analytics is just a complement to the existing methodology of data analysis.
How Does Streaming Analytics Work?
Appreciating streaming analytics requires breaking it down into its component parts to see precisely how this methodology achieves its goals. The basis of streaming analytics comes from a technology known as Event Stream Processing (ESP). ESP is a dedicated processing service that ingests streaming data as it appears before it goes into storage. Each IoT device would transmit their data at their own pace to the ESP system. The ESP would then take that data and run continuous queries on it in real-time. The results are then passed to a subscriber service, which distributes the results in a human-readable form or outputs a flag to sensors to update users.
How Can a Business benefit from Streaming Analytics?
There are evident benefits for implementing analytics that can offer real-time solutions to problems. Among these include:
- Business Process Analysis: IoT devices are useful in keeping track of production quality and shipping. By utilizing real-time analytics, a business could determine methods of improving its process efficiency, and making its shipping system more customer-centric.
- Dealing With Preventable Losses: IoT devices have already made their way into supply chains for several manufacturers. With real-time data updates, these companies can track the movement of stock and refine how they deliver products to different locations. Several inventory management systems already offer interfacing with IoT devices to keep a minimum available stock.
- Competitive Advantage: Technology, if utilized correctly, can offer a competitive edge to a business. IoT data coming into a business can be used alongside streaming analytics to give insight into current trends as they happen. Businesses can pivot to deal with increased demand much faster than they do with batch-processed data, potentially giving them a leg-up on their direct competition.
- Visualization of Data: Most executives within a business don’t see data the same way that data scientists do. Bridging that gap is essential to communicating those insights to people who can influence the company’s policies. Real-time processing enables executives to get access to insights at a much more rapid pace than collective or batch processing means. The more efficient production of these insights allows the company to respond to upcoming threats of opportunities that much faster.
The Future of Business Data Processing
Business data is dynamic, and because of this property, it sees companies changing and adapting their business processing model to meet new challenges within the space. Streaming analytics meshes well with the idea of IoT, but it isn’t the only thing for which companies can use streaming data. Sources of data might be things like social media updates or real-time sales data from the market. The potential for the technology is immense. If businesses want to benefit from the use of streaming analytics fully, they need to figure out in which data collection channel the methodology would perform the best.
-
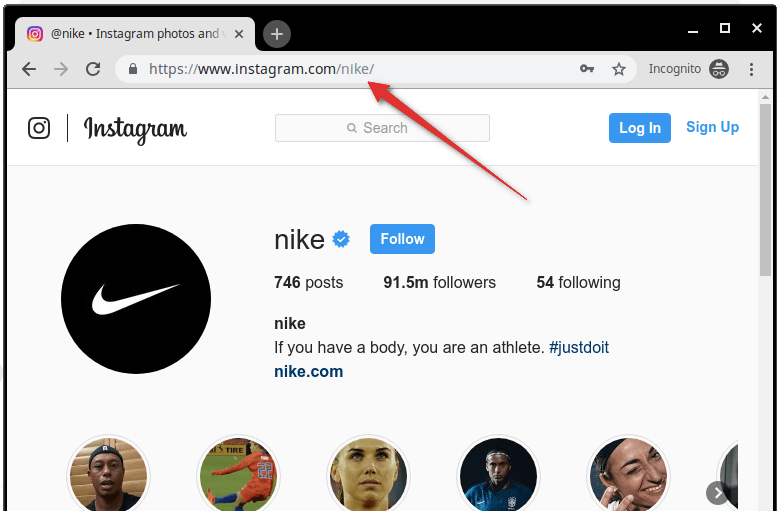
 Marketing Tips3 days ago
Marketing Tips3 days agoWhat is my Instagram URL? How to Find & Copy Address [Guide on Desktop or Mobile]
-
 Business Imprint4 days ago
Business Imprint4 days agoAbout Apple Employee and Friends&Family Discount in 2024
-
 App Development4 days ago
App Development4 days agoHow to Unlist your Phone Number from GetContact
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoOpen-Source GPT-3/4 LLM Alternatives to Try in 2024
-

 Crawling and Scraping5 days ago
Crawling and Scraping5 days agoComparison of Open Source Web Crawlers for Data Mining and Web Scraping: Pros&Cons
-

 Grow Your Business3 days ago
Grow Your Business3 days agoBest Instagram-like Apps and their Features
-

 Grow Your Business5 days ago
Grow Your Business5 days agoHow to Become a Prompt Engineer in 2024
-
Marketing Tips3 days ago
B2B Instagram Statistics in 2024



